Present perfect simple and continuous
What is the present perfect tense?
What is the difference between the perfect simple and the perfect continuous?
If you have ever wondered this, you have come to the right place.
In today’s blog post I’ll be talking about the present perfect, how to use it and when we use it!
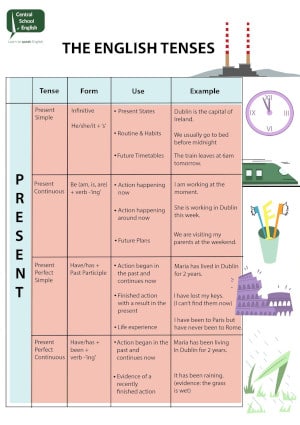
Present perfect simple
The present perfect tense is unusual as it doesn’t just refer to the present but it refers to an action that either began or happened in the past. That’s right, the past!
Try get your head round that one!
There are 3 general uses of the present perfect simple:
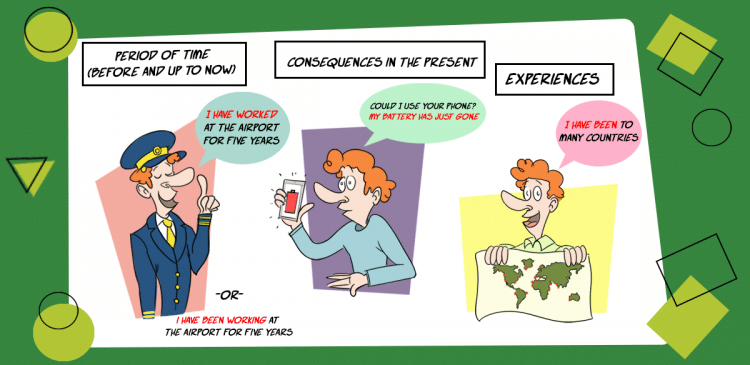
1. When we are thinking about time before and up to now (a period of time).
2. Actions in the past that have a consequence in the present.
3. To speak about our experiences.
Present perfect simple
subject + have + past participle
Period of time
As we have just seen we use the present perfect for a period of time before and up to now.
This means something started in the past and is still happening now. Think of this sentence:
“I have lived in Ireland for 1 year.”
This means I moved to Ireland one year ago and now I am still in Ireland. Look at some other examples:
“She has worked there for 1 month.”
“I have studied at the school for 3 months.”
The word ‘for’ is used to express the period of time. In the examples above, we used : for 1 month, for 3 months.
Apart from this, we can also use the word ‘since’. It is important to notice, however, that if we use the word since, we must say when the action started and not the period of time. We are still talking about the period of time but referring to the starting point.
For example: “I have lived in Dublin since last year /1 year ago/ 2020 etc.”
The structure for the present perfect is : Subject + have + past participle
If you want to know the duration of an action that is still in progress, you can ask:
“How long have you studied at the Central school of English?”
We start the question with ‘How long’ and then add: have + subject + past participle
Consequences of a finished action in the present
In addition to using the present perfect to talk about the duration of an action, we can also use it to talk about something we did in the past which has a consequence in the present. Think about the following sentence:
“Could I use your phone? My battery has just gone.”
Here we have a situation where the person needs to use somebody else’s phone as the consequence of their battery dying.
“I have butterflies in my stomach. I think I have fallen in love” – consequence: feeling butterflies in his stomach
“I have spent too much money this week, now I’m poor.” – consequence: being poor
To speak about our experiences
We often want to share our experiences with others and we often use the past simple to do that but when we want to emphasize that we have indeed done an action in our lives we commonly use the present perfect. Think of the following question:
“Have you ever been to London? I would love to go there.”
“Yes, I’ve been there twice. I’ve also been to the US.”
To make a question we use: Have + subject + (ever)past participle
To make a sentence, use the same structure as before. We might add the number of times we have been somewhere or done something: “I’ve been there once/twice etc.” or we may simply say it without stating how many times we have done it: “I’ve gone jet skiing”.
We use ever in questions but we don’t use it in positive answers. If you want to add something to emphasize you have done it you can add the word ‘before’ at the end instead:
“I’ve gone jet skiing before.”
This is very common to use with the present perfect along with already: “I’ve already been to Paris.”
If you wanted to say you don’t have experience of that you can use the word ‘never’:
“I have never been to the USA”
Just remember to put never after the word have.
Test Yourself
Think about how you would answer the following questions.
- Have you ever been to California
- How long have you lived where you live now?
- Have you ever met a famous person?
- If you have spent too much time watching Netflix, what might happen?
Present perfect continuous
Are you still here? Good!
So far, we have talked about the uses of the present perfect simple, but now we are going to talk about the present perfect continuous.
We use the present perfect continuous to talk about: the duration of an action up to now.
In other words, we emphasize how long an action has been in progress.
If you started studying 1 hour ago and you are still studying (the action is still in progress), you say:
“I have been studying for 1 hour”
Similarly to the present perfect simple when we talk about the duration we use for and since.
Look at some more sentences:
“I have been learning English since I was a child”
“She has been trying to finish her homework for 3 hours.”
“They have been talking on the phone for 30 minutes.”
The structure for the present perfect continuous is:
Subject + have/has been + present participle(ing) + time period
Maybe you are now asking yourself “So, what’s the difference between the present perfect simple and the present perfect continuous?
Well, when we are talking about the duration of an action, there is no real difference! For example, we can say:
Sonia has lived in Dublin for 2 years.
or
Sonia has been living in Dublin for 2 years.
There is no difference between these two sentences!
However, when we talk about the consequence of a past action, we cannot use the present perfect continuous. For example, we say:
Dave has lost his keys.
We cannot say:
Dave has been losing his keys.
When we talk about our life experience, we cannot use the present perfect continuous. For example, we say:
Isabel has travelled around the world several times.
We cannot say:
Isabel has been travelling around the world several times.
There is another use of the present perfect continuous – to talk about evidence now of a recent activity. For more information about this go to this blog post.
Present perfect continuous
subject + have/has been + present participle
We use the present perfect continuous to talk about how long an action has been in progress
Test Yourself
Choose the correct answer.

Vocabulary
Wonder: to think about something
To have butterflies in your stomach: a nervous feeling in your stomach, especially when you are excited or in love
Idioms
Get your head round something: be able to understand something.
Example: I can’t get my head round this book, it’s too confusing
Could you get your head round all that? Hopefully it helped you to understand the present perfect more.
Thank you for reading and feel free to share. You’ll find more English grammar tips elsewhere on our site and if you’d like information on our online English courses live from Dublin, please do not hesitate to contact us.